FLUOROSCOPY
Fluoroscopy the origin of fluoroscopy can be traced back to the eighth number 1895 when William Conrad wrong the notice a barium platinocyanide screen fluorescing as a result of being exposed to x-rays fluoroscopy is a radiological examination which uses x-rays and a fluorescent screen or a detector to issue a lies the internal structures of the body in real-time so we are going to see the objectives of fluoroscopy
The principle of conventional fluoroscopy to understand the fluoroscopic imaging chain understand how fluoroscopic images can be acquired using image intensifiers understand types of fluoroscopic equipment used in a hospital now what is fluorescence we were talking about fluoroscopic imaging
a machine so we need to know about fluorescence is a phenomenon where certain materials emit visibly light in response to some stimuli the stimuli can be x-rays or electromagnetic grace and the emitted light that is coming out from this material stops soon after the stimuli are stopped in the small picture you will be able to see light emission from a fluorescent screen in an early fluorescence fluoroscopy machine conventional fluoroscopy this was used for over more than 100 years so when x-rays passed through a patient they are attenuated by different internal structures of the body and casts a shadow of the structures on the fluorescent screen in this photograph,
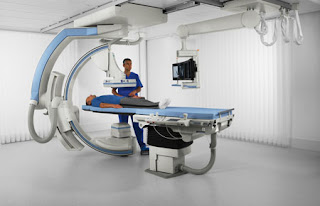
we can see a radiologist imaging a lady who is probably swallowing barium and he's seeing the internal structures of the body with the help of an x-ray machine as well as a fluorescent screen here this illustration also you can see an x-ray tube a couch where a patient can be lying down and then there is a fluorescent screen on top of it is a lead glass the earlier conventional fluoroscopy machines had dim fluoroscopic images and that requires dark environment so eyes have to get adapted to dark environment so when you go into a fluoroscopic room the entire room is switched off all the lights are switched off finally the eyes get adapted to this dark environment it takes about five minutes after that we see this dim image of a fluoroscopic image as seen in this image a tinted glass is placed behind the fluorescent screen for radiation protection purpose so what is the advantage of this conventional fluoroscopy is its simplicity and cost-effectiveness the disadvantages it can impart high radiation dose to the patient as well as others who are there in the room to visualize the image one has to stand on the path of the primary beam and the problem is it requires feebly illuminated room and requires dark adaptation next we move on to a fluoroscopic imaging chain.
Conventional fluoroscopy works but in the case of image intensifiers imagine as fires were introduced in the year 1950s it allows fluoroscopic images to be miscible under normal lighting conditions.
The patient some of the safety checklists in fluoroscopy are to obtain patient history about previous radiation exposure insurer operators and personnel where well-fitted lead aprons thyroid shields and protective eyewear position hanging table shields and overhead shield prior to the procedure in some cases used ultrasound imaging impossible position the detector which is the III has close to the patient as possible for cm type fluoroscopic units maximize the distance from the radiation source use the exposure pedal sparingly use pulsed rather than continuous fluoroscopic mode whenever possible so that we have low doses in part of the patient when low doses are imparted to the patient it will also reduce the radiation dose quatre to the operator's review and save anatomy with the last image hold rather than with live fluoroscopy whenever possible position and column it with fluoroscopy off tapping on the pedal to check the position column it tightly excludes eyes thyroid breast and Gounod's when possible minimize the use of electronic magnification use digital zoom whenever possible I just acquisition parameters to achieve lowest dose necessary to accomplish procedure you slow as those protocol possible for patients eyes lower frame rate minimize magnification radios length of the run operator and personnel hand should be out of the beam in case of using power injector or extension tubing if hand injecting be careful to synchronize the power injector while the images are taken move the personnel away from the table or behind protective shields during acquisition minimize overlap of a field on subsequent acquisitions plan and communicate in advance the number and timing of acquisitions contrast parameters patient positioning suspension of respiration with radiology and sedation team to minimize improperly.


Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any issue regarding articles just ask