FLUOROSCOPY
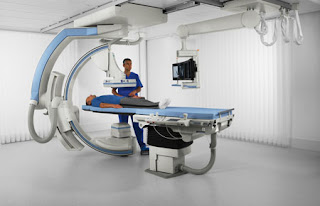
Fluoroscopy the origin of fluoroscopy can be traced back to the eighth number 1895 when William Conrad wrong the notice a barium platinocyanide screen fluorescing as a result of being exposed to x-rays fluoroscopy is a radiological examination which uses x-rays and a fluorescent screen or a detector to issue a lies the internal structures of the body in real-time so we are going to see the objectives of fluoroscopy The principle of conventional fluoroscopy to understand the fluoroscopic imaging chain understand how fluoroscopic images can be acquired using image intensifiers understand types of fluoroscopic equipment used in a hospital now what is fluorescence we were talking about fluoroscopic imaging a machine so we need to know about fluorescence is a phenomenon where certain materials emit visibly light in response to some stimuli the stimuli can be x-rays or electromagnetic grace and the emitted light that is coming out from this material stops soon after the stimuli ar...






